We bring to you the evolution of Electric Vehicles from 1884 to 2022.
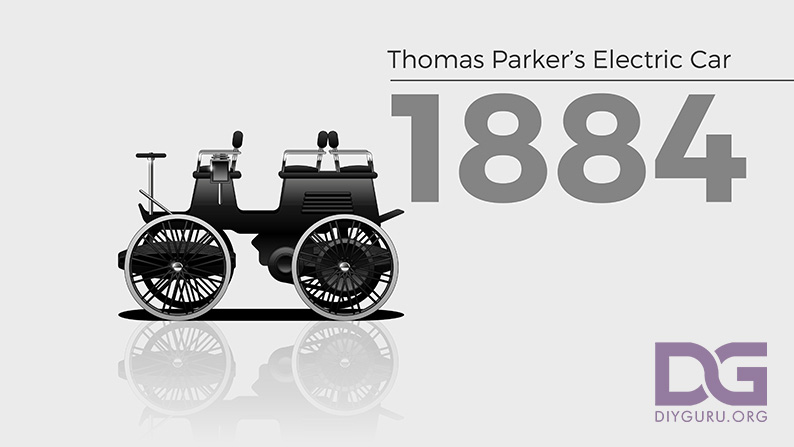
1884 – Thomas Parker’s electric car
English inventor and industrialist Thomas Parker’s first patented invention is a modified steam pump. Still, he was driving to work in Wolverhampton in an electric car that he designed and built in 1884, ten years before Britain’s first taste of a petrol-powered car.
Parker has a knack for fuel-efficient and clean-burning vehicles, which led him to create the first production electric car. He even designed a steam generator to recharge his EV’s lead-acid battery pack.
1888 – Flocken Elektrowagen
Historians regard the Flocken Elektrowagen as the first real electric car. First built in 1888, the Elektrowagen was based on a chassis similar to Gottlieb Daimler’s motorized carriage, although the Elektrowagen came with an electric motor.
1890 – William Morrison electric carriage
Scottish chemist William Morrison’s electric carriage is the first practical horseless carriage built in the United States. It can carry up to twelve passengers on three bench seats and a 20-mph top speed.
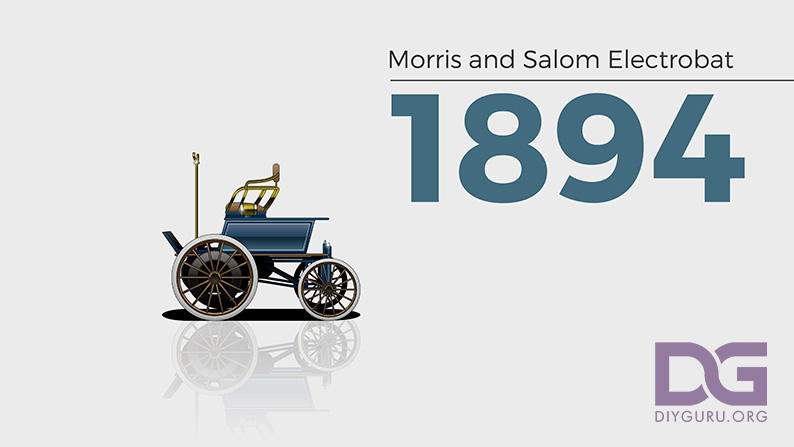
1894 – Morris and Salom Electrobat
Mechanical engineer Henry G. Morris and chemist Pedro G. Salom founded the first electric car company in America, the Morris & Salom Electric Carriage and Wagon Company. Their first vehicle is the Electrobat with two 1.5-horsepower electric motors, 25 miles of range, and a top speed of 20 mph.
1897 – Bersey electric taxicab
British electrical engineer Walter Charles Bersey created an electric taxicab in 1896. The first batch of 12 cabs entered service for the London Electrical Cab Company in 1897. Still, unnecessary damage to the chassis, wheels, and tires due to the battery pack’s excessive weight prompted Bersey to withdraw the cabs from service after two years.
1897 – Hansom cab
Interestingly, the Hansom cab is built by Henry Morris and Pedro Salom, founders of the Electric Carriage and Wagon Company. After Isaac Rice acquired the company to form the Electric Vehicle Company, twelve Hansom cabs roamed Manhattan’s streets until 1899.
1898 – Riker electric vehicle
Andrew L. Riker designed the Riker electric car in 1898. Built in small numbers by the Riker Electric Vehicle Company until 1901, the Riker EV won the first automobile race around a United States track.
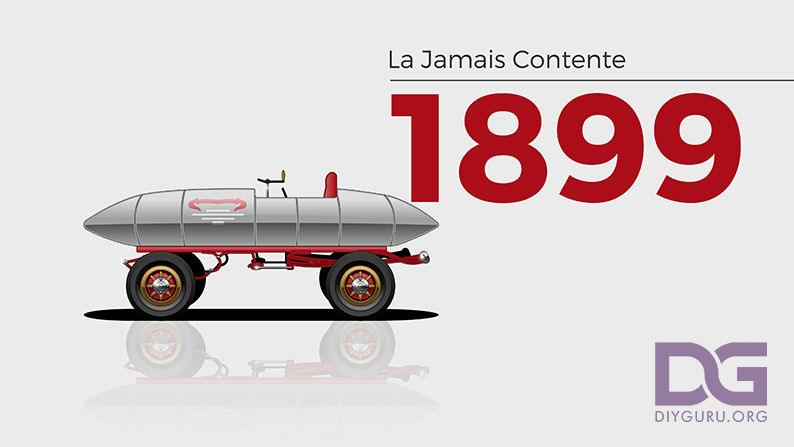
1899 – La Jamais Contente
The La Jamais Contente (The Never Satisfied) is a torpedo-shaped electric vehicle built in Belgium in 1899. Driven by Belgian driver Camille Jenatzy, it was the first road vehicle to go over 62 mph (100 kph) courtesy of two 25 kW direct-drive Postel Vinay electric motors.
1899 – Baker Electric
The very first Baker two-seat electric vehicle is Thomas Edison’s first car. Edison also designed the nickel-iron batteries that were standard in some Baker electric vehicles.
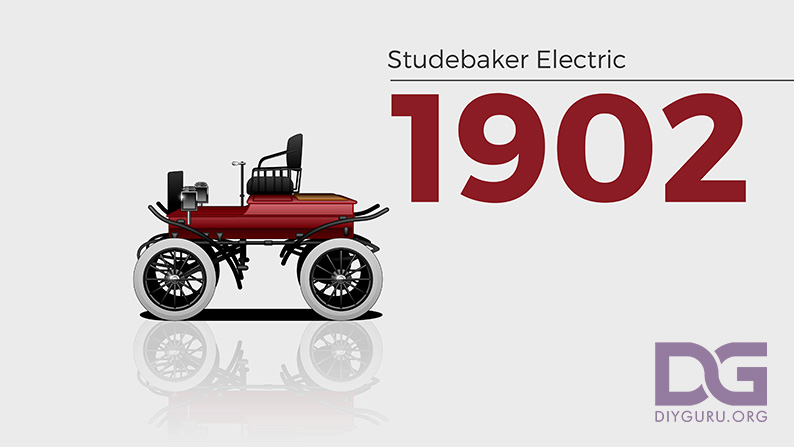
1902 – Studebaker electric car
Before building gasoline vehicles in 1904, American wagon maker Studebaker entered the automotive industry in 1902 with a battery-powered electric car. Studebaker continued building electric vehicles until 1912 before shifting exclusively to gasoline-powered automobiles.
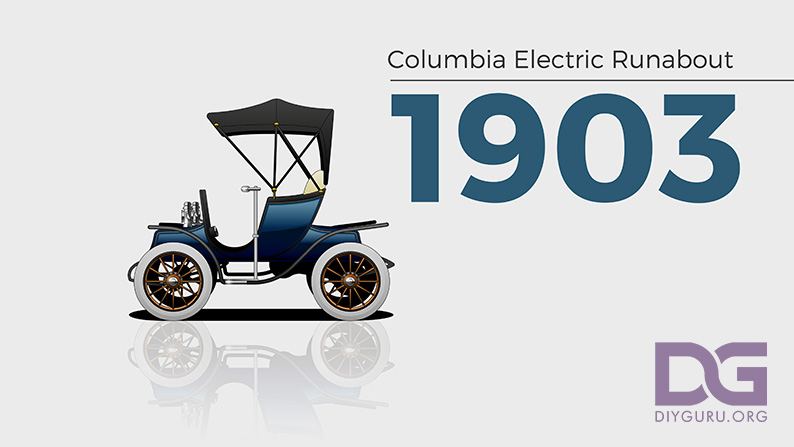
1903 – Columbia Electric Runabout
The Columbia Runabout is a horseless carriage with tiller steering, a chain-drive electric powertrain, and a three-speed transmission. It also came with brakes on the rear wheels that rang a bell when the vehicle reaches a full stop.
1904 – Baker Runabout
The Baker Runabout is a two-seat electric car with centrally-placed electric motors, an armored wood frame, and a 12-cell battery pack. It weighed 650 pounds and had less than one horsepower.
1904 – Woods Queen Victoria Electric
The Woods Queen Victoria is a carriage-style electric car with seating for two. It has two electric motors and a four-speed transmission for a top speed of 18 mph.
1906 – Babcock Electric Car
The Babcock electric car can seat up to three adults. It has a 2.5-horsepower motor, an 18 mph top speed, and a range of 50 miles per full charge. It also came with four elliptic springs for better ride comfort.
1907 – Baker Electric Truck
Baker had seventeen electric models in its lineup by 1907, but the biggest is its range of five-ton electric trucks. Baker electric trucks were designed and created for business owners and were sold until the company’s demise in 1914.
1907 – Detroit Electric
Produced in Detroit by the Anderson Electric Car Company from 1907 until 1939, the Detroit Electric car had a top speed of 20 mph. It also came with a rechargeable lead-acid battery pack, but Edison’s nickel-iron battery pack became a $600 extra from 1911 to 1916.
By 1908, the Ford Model T was the first gas-powered vehicle to be mass-produced on moving assembly lines. The Model T or ‘Tin Lizzie’ came with a 20-horsepower 2.9-liter inline four-cylinder gasoline engine, a three-speed transmission, and rear-wheel drive.
1910 – Baker Electric Coupe
Primarily marketed as an electric luxury car for the ladies, the Baker Electric Coupe seats up to four passengers. It came with black paint and a choice between green, maroon, or blue panels.
In 1912, Ford’s Model T had base prices starting at $650 while an electric car sold at around $1,750. This price disparity is among many reasons behind the dwindling popularity of electric vehicles. For instance, the Baker Electric Coupe sold for $2,800 in 1910.
1912 – Argo Brougham
The Argo Brougham is a four-passenger electric vehicle with up to 75 miles of range per charge. It came with a pair of Westinghouse electric motors for a top speed of 20 mph.
1914 – Rauch and Lang Brougham
Rauch and Lang started by making carriages and coaches in 1860 before shifting to electric vehicles by 1908. The Brougham is a four-seat EV with a fold-down tiller and an 80-volt electric motor.
The electric car slowly faded to oblivion between 1915 to 1954, partly due to the Ford Model T and its affordable $650 base price. However, there were other factors at play. Road infrastructures were significantly improving by the early 1920s, spurring the need for faster vehicles with greater range.
American inventor Charles Kettering invented the electric starter in 1912, eliminating the need to dangerously crank gasoline engines by hand. And by 1897, Milton O. Reeves and Marshall T. Reeves invented the first muffler to reduce petrol engine noise significantly. The worldwide discovery of massive crude oil deposits led to cheaper petrol and reduced a petrol-powered car’s operating costs.
Spurred by the global energy crisis and growing concern against the effects of global warming and hydrocarbon pollution, interest in electric cars saw a resurgence in the early 60s to the late 70s.
1959 – Henney Kilowatt
The Henney Kilowatt was produced from 1959 to 1960. The Henney Motor company sold 47 examples of the Kilowatt to electric utility companies across the United States. It had a top speed of 60 mph and a 60-mile range.
1965 – Scottish Aviation Scamp
The Scamp is a small electric city car concept built by Scottish Aviation in 1965. The company produced 12 pre-production models and a single prototype between 1964 and 1966. However, quality issues made the Scamp ‘unfit for purpose’ by the UK’s Electricity Council.
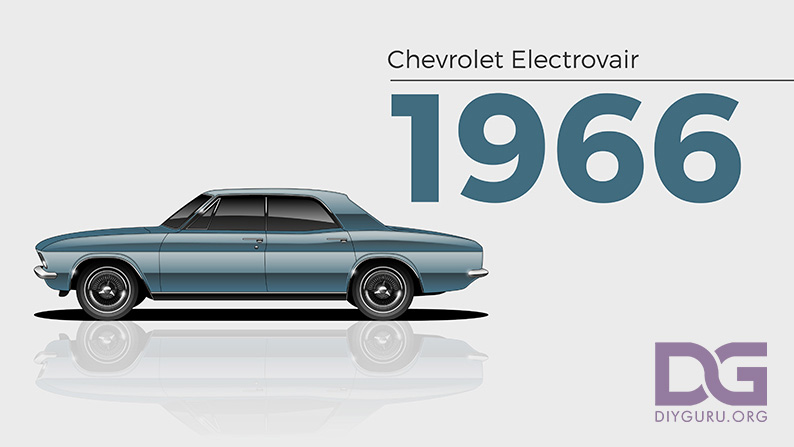
1966 – Chevrolet Electrovair
General Motors was silently experimenting with electric cars in the 1960s. Based on the second-generation Chevy Corvair, GM built the Electrovair as a proof of concept. The Electrovair has a top speed of 80 mph and a range of 40 to 80 miles.
1967 – AMC Amitron
The AMC Amitron results from a collaboration between the American Motors Corporation and Gulton Industries in 1967. The concept featured regenerative braking to drip-charge its 22.5 kWh lithium-nickel-fluoride batteries.
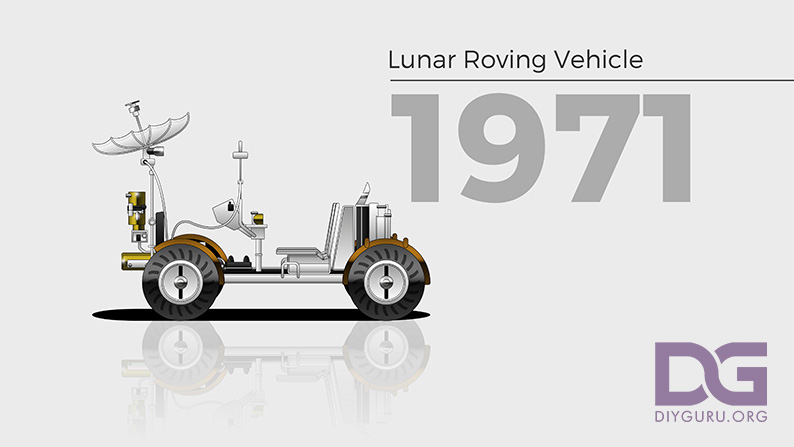
1971 – Lunar Roving Vehicle
Before Elon Musk thought about launching a first-gen Tesla Roadster into orbit, the Lunar Roving Vehicle or Moon buggy is the first all-electric vehicle to land on the Moon. Built by Boeing, the Moon buggy has a top speed of 11.2 mph and served missions for Apollo 15, 16, and 17.
1972 – BMW 1620E
The 1972 BMW 1620e is the first electric car to wear the BMW propeller badge. It came with a 32 kW Bosch electric motor and twelve 12-volt Varta batteries. It has a range of 18 miles at speeds not exceeding 31 mph.
1973 – Enfield 8000
The Enfield 8000 is a two-seat electric city car. It has a single 6 kW electric motor powered by lead-acid batteries, good enough for a range of 40 miles and a top speed of 48 mph. Enfield Automotive built 120 units of the Enfield 8000, 65 of which were utilized by the Electricity Council in South England.
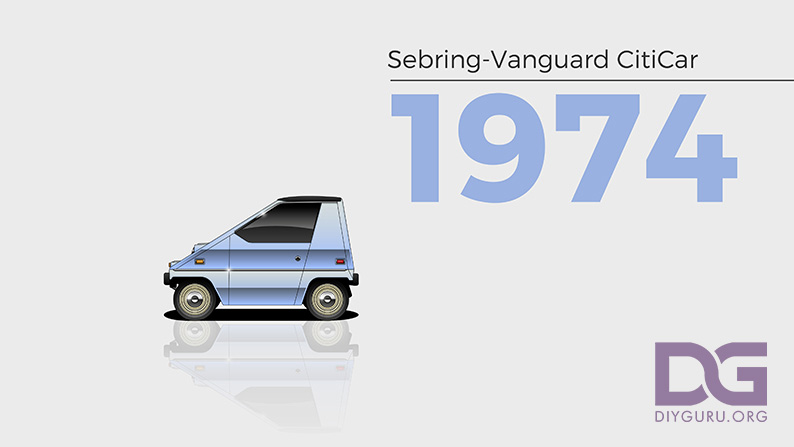
1974 – CitiCar
The CitiCar was produced between 1974 and 1977 by Sebring-Vanguard Inc. The company built 4,444 units of the CitiCar and is the most in North America since the 1940s, a record that stood until the Tesla Model S came into the picture.
1974 – Zagato Zele Elcar
Zagato produced less than 500 units of the Zele or Elcar between 1974 to 1976. It has a single electric motor driving the rear wheels and up to 50 miles of range.
1985 – Sinclair C5
It may look like a toy, and it probably is. The Sinclair C5 is a battery-electric tricycle with a 12-volt lead-acid battery and 20 miles of range.
1990 – GM Impact electric concept
The Impact Concept is the precursor to General Motors EV1 electric vehicle. The concept has an integrated motor and single-speed transmission mounted in the front, producing 137 horsepower and a top speed of 183 mph.
1991 – Kewet electric car
Kewet is the reincarnation of the CitiCar by Sebring-Vanguard and spans six generations from 1991 to 2013. The Kewet Model 1 has a 5 kW electric motor and a four-speed manual gearbox.
1993 – Chrysler TEVan
The California Air Resources Board (CARB) began pushing for lower emission and clean-burning vehicles in the early 1990s. Chrysler was among the first to respond with its TEVan, producing 56 units from 1993 to 1995. It offers seating for five and has a top speed of 70 mph.
1995 – Solectria Force
Take a Geo Metro sedan, replace the internal-combustion engine with a three-phase AC motor, and install a 156-volt battery pack and single-speed gearbox. The result is Solectria Force, a compact electric car with a top speed of 68 mph and a range of 43 miles.
1996 – GM EV1
General Motors produced 1,117 units of the EV1 between 1996 to 1999. It earns the distinction of becoming the first mass-produced electric vehicle from a legacy automaker and is the first electric car designed by the GM from scratch.
1996 – Solectria Sunrise
The Solectria Sunrise achieved 217 miles of range on a single charge, enough distance to cover a trip from Boston to New York. During the 1996 American Tour de Sol competition, the Sunrise achieved 375 miles of range, making it the first long-range electric car. However, Solectria only built several prototypes of Sunrise.
1997 – Chevrolet S-10 Electric
The Chevy S-10 Electric is an electric variant of the carmaker’s S-10 pickup truck. It has an 85 kW liquid-cooled AC induction motor based on GM’s EV1. It achieves 33 miles of range with a 16.2 kWh lead-acid battery, but the range improves to 72 miles with a 29 kWh nickel-metal hydride battery.
1997 – Honda EV Plus
Honda produced 300 units of the EV Plus from 1997 to 1999. It’s the first EV from a major automaker to use nickel-metal hydride batteries. It has a single brushless DC electric motor and achieves 80 to 105 miles of range.
1997 – Toyota RAV4 EV
Toyota produced the first-gen RAV4 EV from 1997 to 2003. It has a 50 kW electric motor producing 67 horsepower and 140 pound-feet of torque. The standard 27.4 kWh NiMH battery pack allows it to achieve up to 95 miles of range.
1998 – Ford Ranger EV
Produced from 1998 to 2002, the Ford Ranger EV has the underpinnings and Regular Cab body style of a gasoline-powered Ranger XL 4×2. Replacing its four-cylinder petrol engine is a 90-horsepower single-speed reduction motor powered by lead-acid or NiMH batteries.
1998 – Nissan Altra EV
Before leading the commercial EV market with the Leaf, Nissan built the Altra EV based on a R’nessa station wagon. Similar to modern EVs, the battery pack is on the floor, while a single electric motor delivers enough oomph for a range of 120 miles.
1998 – Global Electric Motorcars NEV
GEM’s neighborhood electric vehicle (NEV) is street legal in nearly 50 U.S. states. Chrysler formerly owns global Electric Motorcars, but Polaris Industries bought the company in 2011. The NEV has a range of 30-100 miles depending on the battery pack.
2004 – Venturi Fetish
Monaco-based electric car company Venturi built the Fetish from 2004 to 2007. Fetish is the first electric sports car in the world, and it initially came with a 180 kW electric motor producing 241 horsepower. The company launched a new version of the vehicle in 2011. It came with a 220 kW motor with 295 horsepower.
2007 – Smart Fortwo EV
The Smart Fortwo EV or Smart Electric Drive first launched in 2007. The first-gen model had a 30 kW electric motor and a range of 68 miles. The second-gen model came in 2011, brandishing 84 miles of range and a top speed of 62 mph.
2008 – BYD F3DM
Chinese automaker BYD launched the world’s first mass-produced plug-in hybrid vehicles (PHEV) in 2008 with the F3DM. It’s a dual-mode compact car with an all-electric range of 37 miles, while its hybrid electric powertrain provides an additional 300 miles of range.
2008 – Tesla Roadster
The Roadster is the first taste of what’s to come from American EV pioneer Tesla. Based on a chassis and body of a production Lotus Elise, the first-gen Roadster has a single electric motor and a 53 kWh battery pack. It goes from zero to 60 mph in 3.9-seconds and has a range of around 244 miles.
2008 – Think City electric car
In 2011, Think City was only one of five electric cars in the world to be crash-tested and highway-certified, along with the Tesla Roadster, Mitsubishi i-MiEV, Smart ED, and the first-gen Nissan Leaf. Think City has a 34 kWh electric motor and a 24 kWh battery to achieve 99 miles of range.
2009 – Mitsubishi i-MiEV
The i-MiEV (Mitsubishi innovative Electric Vehicle) is an all-electric version of the Mitsu i Kei car. It also sold in Europe as the Peugeot iOn and Citroen C-Zero. The i-MiEV earns the distinction of being the world’s first highway-capable, mass-produced electric car. It has a top speed of 80 mph and has a range of 62 mph.
2010 – Nissan Leaf
The Nissan Leaf entered the market in 2010 with a paltry 73 miles of range and a small 24 kWh lithium-ion battery pack. From 2016, the Leaf gained a larger 30 kWh battery pack to improve the driving range significantly. The current second-gen Leaf has a 40 kWh or 62 kWh battery to generate 151 to 226 miles of range.
2011 – Chevrolet Volt
The Chevrolet Volt is a plug-in hybrid manufactured by General Motor. It is marketed in rebadged variants as the Holden Volt in Australia and New Zealand, the Buick Velite 5 in China, and with a different fascia as the Vauxhall Ampera in the United Kingdom. It’s also called the Opel Ampera in the remainder of Europe. Volt production ended in February 2019.
2011 – Renault Fluence Z.E.
Unlike the Leaf and Volt, Renault’s Fluence Z.E. is an all-electric version of its Fluence compact sedan. It’s the first modern electric car to gain a swappable battery pack, and it initially came with a 22 kWh lithium-ion battery that achieves 115 miles of range.
2011 – Wheego Whip
Produced from 2011 to 2013, the Wheego Whip LiFe has a 30 kWh lithium iron phosphate battery powering a small 45 kW electric motor. It has a top speed of 25 mph and a range of 100 miles.
2011 – Mia Electric
French EV maker Mia Electric introduced its first electric car in 2011. It has a 9.7 kWh electric motor drawing power from an 8 kWh lithium-iron-phosphate battery pack. It has a top speed of 60 mph and achieves 56 miles of range.
2011 – Volvo C30 DRIVe Electric
Based on a production C30 coupe, the Volvo C30 DRIVe Electric has a standard 82 kWh electric motor and a 24 kWh lithium-ion battery pack. It has a top speed of 81 mph, goes from zero to 31 mph in four seconds, and an all-electric range of around 93 miles.
2011 – Ford Focus Electric
Riding on a third-generation Ford Focus hatchback’s body style and underpinnings, the electric model initially came with a 23 kWh liquid-cooled lithium-ion battery, good enough for 76 miles of range. In 2017, it got a larger 33.5 kWh battery to deliver 115 miles of range.
2011 – BYD e6
The BYD e6 is an all-electric five-door compact MPV. With an 80 kWh battery pack, BYD claims a driving range of 248 miles and a top speed of 100 mph.
2011 – Bollore Bluecar
Pininfarina is behind the Bollore Bluecar’s sleek body space. It has a 30 kWh lithium metal polymer (LMP) battery pack and a supercapacitor to deliver 160 miles of urban driving range. With a 50 kW electric motor pumping out 67 horsepower, it achieves a top speed of 75 mph.
2012 – Tesla Model S
The Tesla Model S kickstarted the EV craze of the modern era. The Model S is a full-size luxury car with either a single motor RWD or dual-motor all-wheel drivetrain. The current Model S Plaid has three electric motors for a combined output of 1,020 horsepower and is the quickest accelerating car in production. It goes from zero to 60 mph in under two seconds and has a top speed of 200 mph.
2012 – BMW ActiveE
Built in small numbers, the BMW ActiveE is based on the 1 Series. It has a 125 kW electric motor and a 32 kWh lithium-ion battery to deliver 151 miles of driving range.
2012 – Coda electric car
The Coda was exclusively sold in California as a four-door electric compact. It has a 100 kW electric motor pumping out 130 horsepower. It also gets up to 125 miles of range with its 31 kWh lithium iron phosphate battery.
2012 – Renault Zoe
The Renault Zoe first came in 2012 and is still sold today. It’s an electric five-door supermini that initially came with a 22 kWh lithium-ion battery pack (130 miles of range). The long-range model arrived in 2016 with a bigger 41 kWh battery for up to 250 miles of range.
2012 – Renault Twizy
If the Zoe is not quirky enough for your discerning taste, the Twizy is a sterling option. The Twizy is a quadricycle with a single asynchronous electric motor driving the rear wheels. Equipped with a 6.1 kWh lithium-ion battery pack, it achieves 56 miles of range on a single charge.
2012 – Roewe E50
The Roewe E50 is a four-seat hatchback with three doors, front-wheel-drive, an 18 kWh battery, and 110 miles of range. It has a top speed of 110 mph.
2013 – BMW i3
The i3 is the first mass-produced zero-emissions vehicle from German carmaker BMW. The i3 is EPA-rated at 81 miles of range with the standard 18.2 kWh battery. Later models got a 27.2 kWh and 37.9 kWh battery for up to 152 miles of range.
2013 – Chevrolet Spark EV
Chevrolet produced the Spark EV from 2013 to 2016. It has a 97 kW permanent-magnet AC motor and a 19 kWh battery to achieve a driving range of 82 miles.
2013 – Fiat 500e
The Fiat 500e was introduced in 2013 and remained on sale to this day. Initial models came with an 83 kWh electric motor and a 24 kWh liquid-cooled battery pack to deliver up to 100 miles of driving range.
2013 – Honda Fit EV
The Honda Fit EV has a lithium-ion battery pack and a single electric motor with a low reduction gearbox from the Honda FCX Clarity fuel cell vehicle. It has a top speed of 90 mph and a range of 70 to 100 miles.
2013 – Mahindra e20
The Mahindra e20 is the successor of the G-Wiz electric car. It has a single electric motor and a lithium-ion battery pack for a top speed of 56 mph and up to 75 miles of driving range.
2013 – Mercedes-Benz SLS AMG Electric Drive
The SLS AMG Electric Drive is an electric variant of the Mercedes-Benz SLS AMG grand touring sports car. It has four electric motors producing a combined 740 horsepower and 738 pound-feet of torque, accelerating from zero to 60 mph in under four seconds.
2013 – Scion iQ EV
The Scion iQ EV or Toyota eQ is produced in limited numbers. It has a 12 kWh lithium-ion battery pack that recharges in three hours and delivers 50 miles of range. It also has regenerative braking and a water-cooled charging system.
2013 – Volkswagen E-up
Volkswagen started offering the E-up electric car in 2013. The first-gen model came with an 18.7 kWh battery to deliver 99 miles of range. The second-gen version arrived in 2019 with a larger 32.3 kWh battery and 160 miles of range.
2014 – BMW Brilliance Zinoro 1E
Based on the underpinnings of a production E84 BMW X1 crossover, the Zinoro 1E is designed for the Chinese market. It has a rear-mounted 125 kW electric motor and a lithium-iron-phosphate battery pack to achieve 93 miles of range and a top speed of 81 mph.
2014 – Kia Soul EV
The first Kia Soul EV entered the market in 2014 and is still in production today. The first-gen model has a 27 kWh battery pack, which grew to 30 kWh by 2018. The second-gen model has a more substantial 54 kWh battery to deliver up to 243 miles of driving range.
2014 – Mercedes-Benz B-Class Electric Drive
Interestingly, the Mercedes-Benz B-Class Electric Drive has a 36 kWh battery pack from Tesla. It has a range of 124 miles and a top speed of 93 mph, courtesy of a single 100 kWh electric motor.
2015 – Tesla Model X
It’s hard to miss the falcon-winged Tesla Model X among a sea of crossovers and SUVs. Available with dual electric motors or a tri-motor Plaid version with 1,020 horsepower and 340 miles of range, Model X remains the benchmark for other electric SUVs.
2015 – Volkswagen e-Golf
Before electrifying the seventh-generation Golf, Volkswagen has been experimenting with battery-powered Golfs since the 1970s. The 2015 e-Golf has a range of 83 miles, while the updated model for the 2017 model year achieves 89 to 120 miles of range.
2016 – Chevrolet Bolt EV
Chevrolet developed the Bolt EV in partnership with LG. Also sold as the Opel Ampera-e in Europe, the Bolt EV has a 60 kWh lithium-ion battery to deliver 238 miles of range. The 2020 model has a beefier 66.0 kWh battery pack to achieve an EPA-rated 259 miles of range.
2016 – Tesla Model 3
The Tesla Model 3 became the world’s best-selling electric car in 2020. Tesla has sold more than 800,000 units of the Model 3 as of December 2020. The current model is available in a single motor RWD or dual-motor AWD variant with up to 353 miles of range.
2016 – Hyundai Ioniq Electric
Initial versions of the Hyundai Ioniq Electric were good for 124 miles of range with a 28 kWh lithium-ion battery pack. The updated 2020 model has a 38.3 kWh battery to deliver 170 miles of range. The Ioniq Electric will soon bow down in favor of the all-new Ioniq 5 crossover.
2016 – NIO EP9
The NIO EP9 has inherited electric learnings from the brand’s Formula E racing team. It’s a two-seat electric sports car with four motors producing a combined 1,341 horsepower. The EP9’s lithium-ion battery pack offers up to 265 miles of range, but it has to be removed from the vehicle before recharging.
2017 – Honda Clarity Electric
Honda has three variants of the Clarity sedan: Fuel cell, plug-in hybrid, and all-electric. The latter was introduced in 2017. It came with a 25.5 kWh battery for up to 143 miles of range.
2018 – Audi e-tron SUV
First seen as a concept at the 2015 Frankfurt Motor Show, the e-tron is Audi’s first mass-produced electric car. It has two electric motors, Quattro electric AWD, and a 95 kWh battery pack offering up to 220 miles of range.
2018 – Electra Meccanica Solo EV
Part car and part tricycle, Electra Meccanica’s Solo EV is a single-seat, three-wheeled electric vehicle. It has a 16.1 kWh battery pack to offer 100 miles of range on a single full charge.
2018 – DS3 Crossback e-Tense
The e-Tense is an all-electric version of the petrol and diesel-powered DS3 crossover. It has a 50 kWh lithium-ion battery and a single electric motor pumping out 136 horsepower and 192 pound-feet of torque. The top speed is 93 mph, while the all-electric range is rated at 191 to 206 miles.
2018 – Jaguar I-PACE
The Jaguar I-PACE won the 2019 World Car of the Year award. It has two electric motors producing a combined 395 horsepower. The standard 90 kWh battery pack has a driving range of 246 miles.
2018 – Hyundai Kona Electric
Kona Electric is the second all-electric vehicle from Hyundai, following the Ioniq EV. The base model has a 39.2 kWh battery pack, while the larger 64 kWh battery achieves up to 258 miles of range.
2018 – Kia Niro EV
The all-electric version of the Kia Niro first came in 2018. Similar to Kona Electric, the Niro EV is available in two battery sizes. The base 39.2 kWh battery achieves 179 miles of range, while the 64 kWh battery has an official EPA range of 239 miles.
2018 – Xpeng G3
The Xpeng G3 is a five-seat electric crossover SUV with a single permanent magnet synchronous electric motor and a 50.5 kWh or 65.5 kWh battery pack. Xpeng claims a range of 249 miles on the NEDC cycle.
2018 – Aion S
The Aion S is an electric four-door compact sedan with a single electric motor. It also has a 58.8 kWh battery pack and up to 317 miles of range.
2019 – Buick Velite 6
The Buick Velite 6 first appeared as a concept in 2016. Manufactured by SAIC-GM under the Buick brand in China, it’s available with one or two electric motors and a 35 kWh or 52.5 kWh battery pack. The smaller battery achieves 187 miles of range, while the Velite 6 Plus with the larger battery is good for up to 250 miles before recharging.
2019 – Drako GTE
The Drako GTE is based on the Fisker Karma. It has four electric motors, 1,200 horsepower, and a top speed of 206 mph. With a 90 kWh battery pack, the Drako GTE has an estimated range of 250 miles.
2019 – GFG Style Kangaroo
What do you get if you cross a supercar with a Baja-inspired off-road truck? The GFG Style Kangaroo has two electric motors producing 483 horsepower. It also has a 90 kWh battery pack for up to 280 miles of driving range.
2019 – Hispano Suiza Carmen
The Carmen is Hispano Suiza’s first production vehicle in over 70 years, and it’s a special one. Borrowing design cues from the one-off H6B Dubonnet Xenia of 1938, Carmen has four electric motors producing 1,019 horsepower. It comes with a 700-cell lithium-ion battery pack to deliver 249 miles of range.
2019 – Karma Revero GT
The Karma Revero GT is a hybrid-electric touring sports car with a 1.5-liter inline three-cylinder gasoline-powered onboard generator. The engine supplies energy to a 28 kWh battery and never drives the wheels. It has two electric motors producing 536 horsepower and an all-electric driving range of 80 miles.
2019 – Porsche Taycan
The Taycan is Porsche’s first all-electric car. It features an innovative 800-volt electrical architecture and a proprietary two-speed gearbox. The Taycan Turbo, Turbo S, and 4S have dual motors and all-wheel-drive. The base Taycan has a single electric motor and rear-wheel-drive.
2019 – Mercedes-Benz EQC
The EQC five-seat electric crossover is the first to arrive in Mercedes-Benz’s family of all-electric EQ vehicles. It has two electric motors and an 80 kWh battery pack for an EPA-estimated 220 miles of driving range.
2019 – Polestar 1 PHEV
Polestar 1 is a plug-in hybrid two-door sports car. It has a petrol engine in the front and two electric motors in the rear axle with a combined output of 600 horsepower. It goes from zero to 60 mph in 4.2-seconds.
2019 – Tata Nexon
The Tata Nexon has a single electric motor producing 127 horsepower and 181 pound-feet of torque. It has a 30.2 kWh battery pack to offer up to 186 miles of range.
2020 – Audi e-tron Sportback
The Audi e-Tron Sportback is a sloppier-roof version of a standard e-tron SUV. It has the same powertrain and 95 kWh battery as the latter.
2020 – Aspark Owl
The goal behind Asprak Owl is to produce the fastest accelerating electric car. It has four electric motors churning out 1,984 horsepower and a 69 kWh battery. The Owl goes from zero to 60 mph in 1.69 seconds and has a top speed of 249 mph.
2020 – Mini Electric or Mini Cooper SE
The Mini Electric’s powertrain I derived from the BMW i3. It has a single 135 kWh electric motor producing 181 horsepower. The standard 32.6 kWh battery pack delivers 146 to 168 miles of driving range on a full charge.
2020 – Tesla Model Y
The Tesla Model Y is a crossover version of the bestselling Model 3 electric sedan. It’s available as a single motor RWD variant or with a dual-motor AWD powertrain offering up to 326 miles of range.
2020 – HiPhi X
Chinese automaker HiPhi is hitting the right spots with its six-seater X electric CUV. It has conventional doors in the front and split falcon-wing and coach doors in the rear. HiPhi X has a 96.0 kWh battery powering two electric motors for an estimated 400 miles of driving range.
2020 – Honda e
The Honda e is a small five-door electric hatchback with retro-inspired styling. It has a single electric motor and a 35.5 kWh battery pack. It goes from zero to 60 mph in 8.3 seconds and offers 137 miles of driving range.
2020 – Ford Mustang Mach E
Forget the Mustang moniker. The Ford Mach-E is a sporty electric crossover sold with two battery sizes, three power outputs, and five trim models. The sportiest and fastest Mustang Mach-E is the GT version with a top speed of 124 mph and 235 miles of range.
2020 – Lexus UX300e
Based on a gasoline-powered Lexus UX crossover, the UX300e has a top speed of 100 mph and up to 249 miles of range with a standard 54.3 kWh battery pack.
2020 – Volkswagen ID.3
The Volkswagen ID.3 is temporarily filling the void of an affordable, mass-produced electric car. The ID.3 makes fair use of a single 200-horsepower electric motor and a choice between a 45 kWh, 58 kWh, or a 77 kWh battery to deliver up to 340 miles of range.
2020 – Volkswagen ID.4
The ID.4 is the second model of Volkswagen’s all-electric ID series. The ID.4 is a five-door SUV with a single rear-mounted electric motor. It’s available with a 52 to 82 kWh battery pack to deliver up to 250 miles of range.
2020 – Volvo XC40 Recharge
The XC40 Recharge is based on a standard petrol or diesel-powered CX40 crossover with dual electric motors producing 402 horsepower and 487 pound-feet of torque. The s78 kWh battery pack is good for 250 miles of range.
2020 – Polestar 2
Unlike Polestar 1, Polestar 2 is an all-electric five-door crossover and is the first production vehicle to feature a Google Android Automotive operating system. It has two electric motors, AWD, and achieves 233 miles of range with its 78 kWh battery pack.
2020 – Xpeng P7
The Xpeng P7 is a four-door midsize electric sedan with fastback styling. Similar to the Tesla Model S, the P7 is available with single or dual electric motors. It achieves 349 miles of range with a standard 80.87 kWh lithium-ion battery pack.
2020 – Pininfarina Battista
Powered by four liquid-cooled electric motors and a 120 kWh battery pack from Croatian hyper EV maker Rimac, the Battista accelerates from zero to 60 mph in under two seconds, a top speed of around 217 mph, and 280 miles of range.
2020 – Rimac C_Two
The Concept Two or C-Two is Rimac’s second electric supercar and is based on the same platform as the Pininfarina Battista. With four electric motors and a 120 kWh battery pack, the C_Two has 1,888 horsepower and 400 miles of range.
2020 – Bollinger B1 and B2
The Bollinger B1 is a sport utility truck, while the B2 is an electric pickup. Both come standard with two electric motors, a 142 kWh battery pack, and around 200 miles of range.
2020 – Audi e-tron GT
The e-tron GT is Audi’s first high-performance electric car. It has two electric motors, AWD, and a 93.4 kWh liquid-cooled battery pack. It goes from zero to 60 mph in 3.5-seconds and has a range of 264 miles.
2021 – Aptera Solar EV
Aptera’s Solar EV has three wheels and an array of solar panels in the roof, which harnesses 40 miles of range on a sunny day. Equipped with a 100 kWh battery pack, the Solar EV’s lightweight construction and minimalist design allow it to travel up to 1,000 miles before recharging.
2021 – Hyundai Ioniq 5
The Ioniq 5 debuted at the 2019 Frankfurt Motor Show as the 45 Concept. It replaces the Ioniq Electric as Hyundai’s entry-level EV and is built on top of its dedicated E-GMP electric platform. Production for the Ioniq 5 commences in 2021, with the first deliveries arriving in early 2022.
2021 – Nissan Ariya
The Ariya is Nissan’s second all-electric production vehicle following the Leaf. The Ariya will be sold in two battery sizes with either front or all-wheel-drive and will feature Nissan’s ProPilot 2.0 autonomous driving system.
2021 – Rivian R1T and R1S
Rivian’s R1T pickup and R1S electric SUV are the most hotly-anticipated electric vehicles to date. In early testing, both models went from zero to 60 mph in under three seconds while having the ability to climb a 45-degree incline and wade through 3.6-feet of water.
2021 – Lucid Air
The Tesla Model S better watch out for Lucid Air. It has two electric motors producing 1,080 horsepower, while its optional 113.0 kWh battery pack and 900-volt architecture allows up to 517 miles of range.
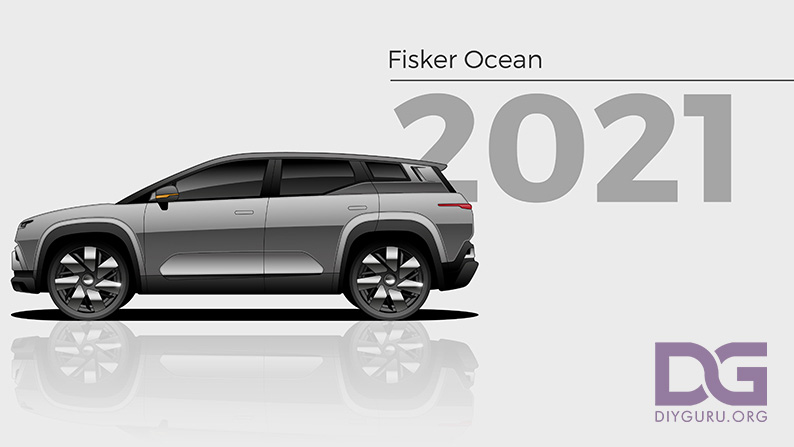
2021 – Fisker Ocean
The Ocean is Henrik Fisker’s attempt at building an all-electric luxury SUV. The Ocean features one or two electric motors and an 80 kWh battery to deliver 300 miles of range. It also has a sustainable interior built using plastic water bottles and discarded fishing nets.
2021 – Lotus Evija
Lotus is only building 130 examples of its Evija hyper EV. It has four electric motors producing 1,970 horsepower and goes from zero to 60 mph in under three seconds. It has a top speed of over 200 mph and 250 miles of range, courtesy of a 70 kWh lithium-ion battery.
2021 – Gumpert Nathalie
The Gumpert Nathalie is unlike any modern electric car. It has a 15 kW fuel cell that feeds on methanol to energise a standard 70 kWh battery. With four electric motors, the Nathalie rushes to 60 mph in 2.5-seconds and has a top speed of 190 mph.
2021 – Tesla Roadster 2.0
The second-generation Tesla Roadster is a long time coming, but it’s worth the wait. It has a single electric motor in the front and two electric motors in the back, with a massive 200 kWh battery pack in the middle. Tesla claims a top speed of above 250 mph and zero to 60 mph in 1.9-seconds.
2022 – Hispano Suiza Carmen Boulogne
The Boulogne is an extreme version of Hispano Suiza’s Carmen EV. It has two electric motors in each rear wheel with a combined output of 1,100 horsepower and 1,180 pound-feet of torque. It goes from zero-to-sixty in 2.6-seconds and has a top speed of 180 mph.
2022 – GMC Hummer EV
What was once known as a symbol of conspicuous consumption has turned into a zero-emissions behemoth. General Motors claims its new Hummer EV will have dual or triple electric motors producing up to 1,000 horsepower and 350 miles of range from its 200 kWh battery pack.
2022 – Cadillac Lyriq
The Lyriq is leading Cadillac’s resurgence in the new era of electrification. The Lyriq will become the second all-electric vehicle from GM and feature its next-gen Super Cruise autonomous driving technology.
2022 – Tesla Cybertruck
Tesla fans can’t wait for 2022 to arrive with the impending arrival of Cybertruck, the most rugged Tesla EV to date. It has an innovative exoskeleton chassis with a single, dual, or tri-motor setup. The latter can push the Cybertruck from zero to 60 mph in under 2.9-seconds.
Is the Future Electric?
Gustave Pierre Trouvé created a portable battery-powered motor for marine propulsion, essentially inventing the outboard engine still in use today. Nowadays charging infrastructures and battery technology are the only factors limiting the full potential of all-electric vehicles.
































































































































 Course work & interactions are 100% online.
Course work & interactions are 100% online.












0 responses on "Evolution of Electric Vehicles from 1884 to 2022"